Safety in Wireless Sensor Networks: Types of Attacks and Solutions
Héctor KASCHEL, José MARDONES, Gustavo QUEZADA
Departamento de Ingeniería Eléctrica, Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad de Santiago de Chile
Avenida Bdo. O’Higgins 3363, Estación Central, Santiago, Chile
Abstract: Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are highly vulnerable in their security. They are generally deployed in hostile environments to collect different kinds of data, so they are exposed to serious physical and software attacks. Therefore, developing methods to increase security becomes an essential aspect of the study of these networks. WSNs are used in military, medical and biological applications, among others. This paper analyzes the security requirements of WSNs, the main attacks, and their main characteristics; finally it reviews some security methods currently proposed or implemented in these networks, and identifies the possible types of security attacks that can affect the layers of the OSI Reference Model.
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), Types of attacks.
>>Full Text
CITE THIS PAPER AS:
Héctor KASCHEL, José MARDONES, Gustavo QUEZADA, Safety in Wireless Sensor Networks: Types of Attacks and Solutions, Studies in Informatics and Control, ISSN 1220-1766, vol. 22 (3), pp. 323-330, 2013. https://doi.org/10.24846/v22i3y201309
Introduction
Wireless Sensor Networks are formed by a large number of small nodes, which consume low levels of energy and are low cost. These sensors are easy to deploy in an area designed for wireless networks performing specific functions. The fact that these networks are formed by a large number of nodes allows them to be used in industrial environments to carry out the control functions. Their configuration makes it possible for the sensors to be located abundantly, at all points of interest, and at a low cost. These kinds of networks also offer the same services and advantages as normal wireless networks. Because of the low cost of the nodes, it is possible to reconfigure them or adapt them to specific access points, providing access to a larger network such as, for example, the Internet.
Rapid technological advances cause products and services to vary constantly, forcing industry to satisfy those variable demands for the number and diversity of products. To fulfil those requirements, industry must develop two basic concepts: flexible manufacturing and processes. In this context, wireless networks can contribute process flexibility by offering mobility and control independent of the physical location of the process. They also offer control for processes in motion or for moving parts; they offer access to places that are inaccessible to wired networks, and provide safety with respect to broken wires. Figure 1 shows the main applications of wireless sensor networks.
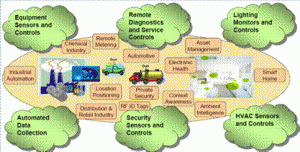 Figure 1. Application of Wireless Sensor Networks
Figure 1. Application of Wireless Sensor Networks
On the other hand, industrial processes must offer high energy availability and efficiency so as to satisfy the associated production requirements. A lack of availability may mean great economic loss caused by stopping some highly important production line, or even worse, the whole production process. Also, the system must have a high level of security so that there is no change in information at any time.
Section 2 analyzes the security requirements; section 3 shows the different types of security attacks and their impact on the wireless sensors; section 4 describes some proposed designs and security solutions used for WSNs; section 5 provides a security approach based on the layers of the OSI Reference Model; and finally section 6 gives the conclusions of this research work.
REFERENCES:
- JAIN, A., K. K. KANT, M. R. TRIPATHY, Security Solutions for Wireless Sensor Networks, Second International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies (ACCT), 2012, pp. 430-433.
- MODARES, H., R. SALLEH, A. MORAVEJOSHARIEH, Overview of Security Issues in Wireless Sensor Networks, Third International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation (CIMSiM), 2011, pp. 308-311.
- SHARMA K., M. K. GHOSE, D. KUMAR, R. PEEYUSH KUMAR, SINGH, V. KUMAR PANDEY, A Comparative Study of Various Security Approaches Used in Wireless Sensor Networks. In IJAST, vol. 7, April 2010.
- JAYDP, S., A Survey on Wireless Sensor Network Security, Technical Report 55-77, International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS) Vol. 1, N°2 August 2009.
- PATHAN, A. S. K. H.-W. LEE, C. S. HONG, Security in Wireless Sensor Networks: Issues and Challenges, The 8th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, ICACT 2006, vol. 2, 2006, pp. 1043-1048.
- DAOJING, H., C. CHEN; CHAN, S. JIAJUN BU, DICODE, DoS-Resistant and Distributed Code Dissemination in Wireless Sensor Networks, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 11, Issue 5, 2012, pp. 1946-1956.
- OUYANG, X., T. BIN, L. QI, Z. JIAN-YI, H. ZHENG-MING, X. YANG, A Novel Framework of Defence System Against DoS Attacks in Wireless Sensor Networks, 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM), 2011, pp. 1-5.
- WANG, B-T. H. SCHULZRINNE, An IP traceback mechanism for reflective DoS attacks, Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Volume 2, 2-5 May 2004, pp. 901-904.
- JIA, G., F. JIAN’AN, X. CHEN, Survey on Secure Data Aggregation for Wireless Sensor Networks, IEEE International Conference on Service Operations, Logistics and Informatics (SOLI), 2011, pp.138-143.
- PFLEEGER, C. P. S. L. PFLEEGER, Security in Computing, 3rd edition, Prentice Hall 2003.
- CHEN, S., G. YANG, S. CHEN, A Security Routing Mechanism Against Sybil Attack for Wireless Sensor Networks, International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing (CMC), Vol. 1, 2010, pp. 142-146.
- YI, S., C. YONGFENG, T. LIANGRUI, A Multi-phase Key Pre-distribution Scheme based on Hash Chain, 9th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), 2012, pp. 2061-2064.
- NEWSOME, J., E. SHI, D. SONG, A. PERRIG, The Sybil Attack in Sensor Networks: Analysis & Defences, Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, ACM, 2004, pp. 259-268.
- SHARMILA, S., G. UMAMAHESWARI, Detection of Sinkhole Attack in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Message Digest Algorithms, International Conference on Process Automation, Control and Computing (PACC), 2011, pp. 1-6.
- CULPEPPER, B. J. H. C. TSENG, Sinkhole Intrusion Indicators in DSR MANETs, Proceedings of the First International Conference on Broadband Networks, 2004, pp. 681-688.
- WANG, W., J. XU, J. WANG, Detection and Location of Malicious Nodes based on Source Coding and Multi-path Transmission in WSN, 11th IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, 2009, pp. 458-463.
- KARLOF, C., D. WAGNER, Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks: Attacks and Countermeasures, Elsevier’s Ad Hoc Network Journal, Special Issue on Sensor Network Applications and Protocols, September 2003, pp. 293-315.
- HARBIN, J., P. MITCHELL, D. PEARCE, Wireless Sensor Network Wormhole Avoidance using Reputation-based Routing, 7th International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), 2010, pp. 521-525.
- TRIKI, B., S. REKHIS, N. BOUDRIGA, Digital Investigation of Wormhole Attacks in Wireless Sensor Networks. Eighth IEEE International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications, 2009, pp. 179-186.
- XUAN, Y., Y. SHEN. N. P. NGUYEN, M. T. THAI, A Trigger Identification Service for Defending Reactive Jammers in WSN, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 11, Issue 5, 2012, pp. 793-806.
- MAHMOOD, A. R., H. H. ALY, M. N. EL-DERINI, Defending Against Energy Efficient Link Layer Jamming Denial of Service Attack in Wireless Sensor Networks, 9th IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), 2011, pp. 38-45.
- HAMID, M. A., M.-O. RASHID, C. S. HONG, Routing Security in Sensor Network: Hello Flood Attack and Defence, to appear in IEEE ICNEWS 2006, 2-4 January, Dhaka.
- SLIJEPCEVIC, S., M. POTKONJAK, V. TSIATSIS, S. ZIMBECK, M. B. SRIVASTAVA, On Communication Security in Wireless Ad-hoc Sensor Networks, 11th IEEE International Workshops on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises, 10-12 June 2002, pp.139-144.
- DU, W., J. DENG, Y. S. HAN, P. K. VARSHNEY, A Pairwise Key Pre-distribution Scheme for Wireless Sensor Networks, Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, 2003, pp. 42-51.
- CHAN, H, A. PERRIG, D. SONG, Random Key Predistribution Schemes for Sensor Networks, In IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Berkeley, California, May 11-14 2003, pp. 197-213.
- ESCHENAUER, L., V. D. GLIGOR, A Key-management Scheme for Distributed Sensor Networks, Proceedings of ACM CCS’02, 18-22 November 2002, pp. 41-47.
- KARAKEHAYOV, Z., Using REWARD to Detect Team Black-hole Attacks in Wireless Sensor Networks, in Workshop on Real-World Wireless Sensor Networks (REALWSN’05), 20-21 June, 2005, Stockholm, Sweden.
- MOON, M., D. S. KIM, JONG SOU PARK, Toward Modelling Sensor Node Security Using Task-Role Based Access Control with TinySec, Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, vol. 2, 2006, pp. 1109-1112.
- KARLOF, C., N. SASTRY, D. WAGNER, TinySec: A Link Layer Security Architecture for Wireless Sensor Networks, 2° International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Baltimore, MD, USA, 2004, pp. 162-175.
- LI, Y., F. LIU, L. DING, Research about Security Mechanism in Wireless Sensor Network, International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing (IASP), 2011, pp. 447-451.
- YEO, D.-G., H.-Y. YOUM, An µTESLA Protocols with Multi-senders Based on a 2-Level XOR Chain with Data-Loss, 10th International Symposium on Tolerance Applications and the Internet (SAINT), 2010, pp. 269-272.
- PANDEY, A., R. C. TRIPATHI, A Survey on Wireless Sensor Networks Security, International Journal of Computer Applications, Vol. 3, N° 2, June 2010, pp. 43-49.
- KASCHEL, H., Y. B. L. SANCHEZ, J. MARDONES, G. QUEZADA, Modelling Sensor Node Security Using Task-Role based Access Control with TinySec, Studies in Informatics and Control Journal. Vol. 20, N° 3, September 2011, pp. 285-292.
 Studies in Informatics and Control – ICI Bucharest
Studies in Informatics and Control – ICI Bucharest